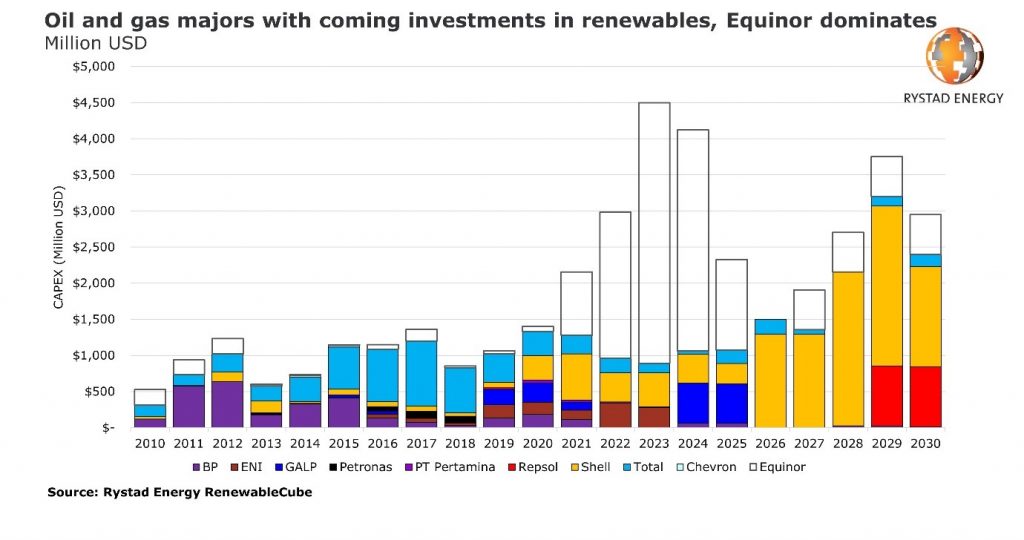
Investments in solar and wind energy projects by the world’s oil majors over the next five years are expected to reach US$17.5 billion, a Rystad Energy analysis finds. But a closer look at the numbers reveals that some US$10 billion, or 57 percent of the amount, is expected to be invested by a single company, Equinor, the only investor whose majority of greenfield capex will be towards renewable energy.
Equinor, the Norwegian state-controlled energy giant, will drive renewable investment among majors, spending US$6.5 billion in the next three years to build its capital-intensive offshore wind portfolio. It is not expected that this forecast will be heavily affected by the fluctuating oil price or capex cuts, as much of the company’s renewable portfolio is already committed, such as the massive Dogger Bank offshore wind project in the UK.
If Equinor is removed from the outlook, however, renewable investments from major oil and gas companies can be seen in a very different light, declining over the next three years. This fall does not even factor in any of the recent capex cuts announced by the majors.
“Recent suggestions of ‘resilient green strategies’ or ‘business as usual’ simply do not carry much weight, with the exception of Equinor. Not until later in the decade do we see an increase in renewable spending from other companies,” says Rystad Energy’s Product Manager for Renewables Gero Farruggio.
After Equinor, the runner-up is Portuguese operator GALP, directing just under a quarter of its greenfield expenditure to green initiatives.
Rystad Energy’s analysis finds that almost all of the renewable investments by oil and gas players will come from just 10 oil majors, which are collectively poised to spend about US$17.5 billion on renewable energy projects over the next five years. This tally, however, pales in comparison to the US$166 billion they are forecast to spend on greenfield oil and gas projects during the same period.
With the notable exceptions of Equinor and GALP, the investments in renewables by the other oil giants will not even match the typical capex requirements of a single oil and gas field in their respective portfolios.
If needed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, a 20 percent capex cut across overall investment portfolios could be achieved while easily avoiding any cuts to renewable projects. GALP and Shell look the most exposed to potential renewable spending cuts, but these companies are not expected to make significant renewable investments in the near term – not before 2024 for GALP and even later for Shell – by which time we expect the oil price will have recovered, thus creating a better environment for investment.
But COVID-19 could also be the catalyst for oil majors to pump more capital into renewables, acquiring assets, developing skills and nurturing the capacity to transition beyond petroleum. “The pandemic is creating a number of distressed sellers and reducing acquisition costs for assets and companies, thereby creating opportunities for Big Oil to accelerate its energy transition through acquisitions. And with E&P companies announcing deep spending cuts, we may yet see a ramp up in renewable investments as recent headlines suggest, facilitated by new mergers and acquisitions,” adds Farruggio.

















